nth_element是stl中的一个库函数,该函数可以从某个序列中找到第 n 小的元素 K,并将 K 移动到序列中第 n 的位置处。不仅如此,整个序列经过 nth_element() 函数处理后,所有位于 K 之前的元素都比 K 小,所有位于 K 之后的元素都比 K 大。
但这个函数与完整排序的区别在于:
1.它只关注第n个,只保证小于该值的元素在其左边,大于等于的在其右边,但并不保证其完全有序。
2.它的时间复杂度在O(N),而许多排序所用的复杂度为O(NlogN)。对于特定的找到第k大数的问题,所花时间是好于排序的。
它的原理思想如图
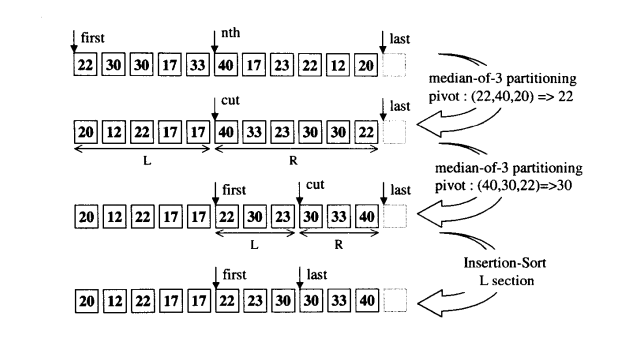
这个算法的思路很像快排中partation函数。首先有一个first ,nth,last,首先找到这三个所在位置值的中位数,这里22,40,20中位数为22。
然后对于22进行第一轮,方法同partation,22则作为锚点。
然后这里找到右端的第一个(如果是数组为0-10装着上图的值),这里右端第一个即数组下标为5的数字40,而传入我们要找的nth也为5(其实即找到0-10中第6大的数),因此其小于等于右端起点,于是进入右段进行下一轮。
下一轮同理40,30,22取30 进行交换使cut两端被分割。
这时候再右端第一个和nth再进入,这时判断到子序列已经不大于3了,直接用插入排序。最后即得到第nth(这里传入nth为5,实际即第六大的数)为22.
以下是代码的解析:
下面是nth_element在本人电脑中stl的源码(可以跳过)
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
nth_element(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __nth,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_Mutable_RandomAccessIteratorConcept<
_RandomAccessIterator>)
__glibcxx_function_requires(_BinaryPredicateConcept<_Compare,
typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type,
typename iterator_traits<_RandomAccessIterator>::value_type>)
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __nth);
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__nth, __last);
if (__first == __last || __nth == __last)
return;
std::__introselect(__first, __nth, __last,
std::__lg(__last - __first) * 2,
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
其中直接讲其核心的__introselect函数部分
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Size, typename _Compare>
void
__introselect(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __nth,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Size __depth_limit,
_Compare __comp)
{
while (__last - __first > 3)
{
if (__depth_limit == 0)
{
std::__heap_select(__first, __nth + 1, __last, __comp);
// Place the nth largest element in its final position.
std::iter_swap(__first, __nth);
return;
}
--__depth_limit;
_RandomAccessIterator __cut =
std::__unguarded_partition_pivot(__first, __last, __comp); //这里函数返回的是分割后右段的第一个元素。后面会详细讲解一下这个的功能
if (__cut <= __nth) //如果右段起点小于等于nth
__first = __cut; //进入右段,对右段进行下次的分割
else
__last = __cut;
}
std::__insertion_sort(__first, __last, __comp);
}这个算法的思路很像快排中partation函数的思路。但对于段长度在3时候,就选择使用插入排序。
这里的关键是__unguarded_partition_pivot函数部分
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline _RandomAccessIterator
__unguarded_partition_pivot(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
{
_RandomAccessIterator __mid = __first + (__last - __first) / 2;
std::__move_median_to_first(__first, __first + 1, __mid, __last - 1, //对first last mid排序找到中位值
__comp); //这里的中位值即下面的pivot点
return std::__unguarded_partition(__first + 1, __last, __first, __comp); //这里即实现了对于类似快排若左边大于pivot则与右边小于pivot的交换
} //并返回的是右端第一个

